Articles categorized as Nerve Damage
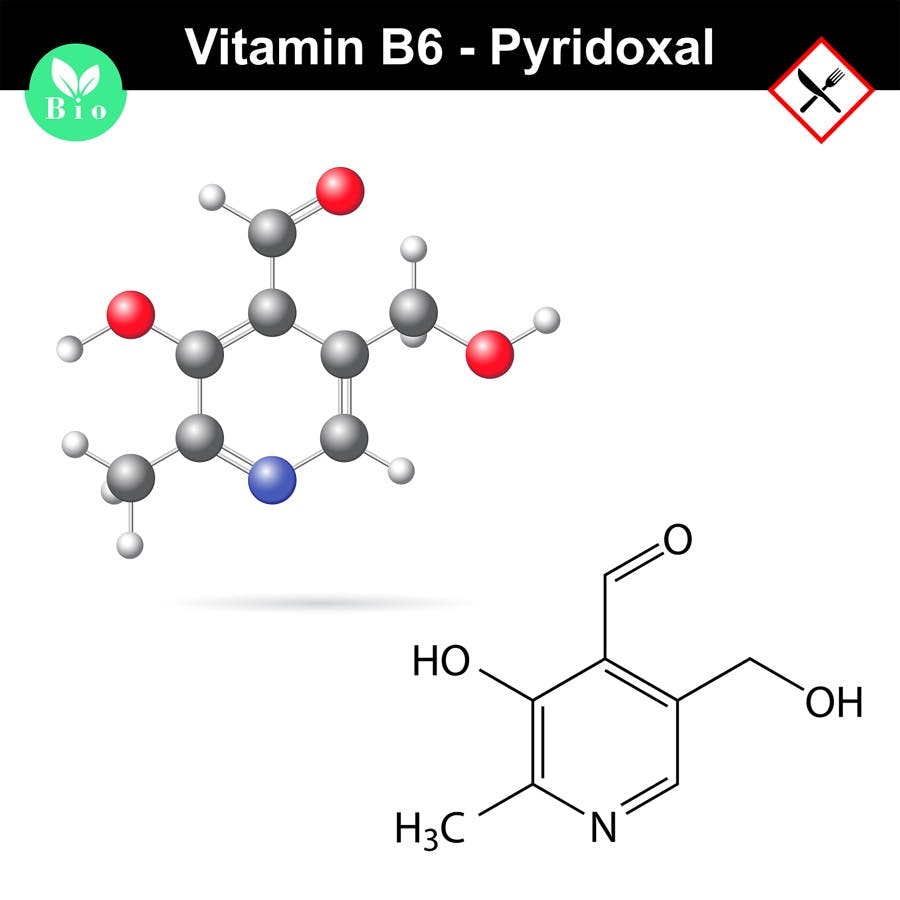
High Doses of Vitamin B6 Could Cause Nerve Damage
High doses of vitamin B6 can lead to neuropathy instead of helping nerve pain heal. Why do these supplements backfire this way?
Do Fluoroquinolone Antibiotics Damage Heart Valves?
The trail of tears from antibiotics like ciprofloxacin (Cipro) and levofloxacin (Levaquin) continues. The latest chapter in this saga: damaged heart valves!
Show 1174: What to Do About Skeeter Syndrome
This week, share your thoughts and learn about skeeter syndrome, how certain common drugs affect your ability to think and statin side effects.
Statins and Nerve Damage (Peripheral Neuropathy): An Overlooked Side Effect!
Is cholesterol necesary for proper nerve function? Most prescribers are unaware of this idea, but statins and nerve damage in type 2 diabetes are related.
Seniors Swear by Marijuana Oil for Pain Relief
Marijuana oil applied to the skin helps one senior with persistent nocturnal foot pain. Others in the retirement community are taking note.
Do People Who Eat Fish Grow Old More Healthfully?
A long-running study suggests that people who eat fish and shellfish regularly are less prone to chronic disease as they age.
Will Benfotiamine Ease Your Foot Pain?
Benfotiamine may help alleviate nerve pain associated with diabetes. A reader wonders if it will help other types of neuropathy as well.
What Makes Turmeric So Wonderful?
Activity against a wide range of chronic diseases, from Alzheimer to cancer to fatty liver makes turmeric so wonderful that it is a very popular supplement.
Will Overdosing on Vitamin B6 Cause Irreversible Nerve Damage?
Diagnosing what is causing neuropathy or nerve pain can be challenging. Sometimes it is caused by too little or too much vitamin B6. Beware of overdosing.
How Can You Overcome Long-Term Tingling?
Uncovering and correcting a thyroid hormone problem and a vitamin deficiency made a long-term tingling sensation disappear.
Blood Pressure Pills Are Contributing to Nerve Damage and Dizziness
Finding ways to control blood pressure without devastating complications can be a challenge.
Could Your Antibiotic Cause You Permanent Nerve Damage?
According to a recent FDAs safety communication, use of fluoroquinolone antibiotics may lead to permanent nerve damage in some patients.
Vitamin Overdose Damages Nerves
When it comes to vitamin B6, it is important to avoid vitamin overdose. Too much pyridoxine can lead to debilitating nerve damage that may take a lot of time to heal.